Installing the Microsoft Teams client on Linux.
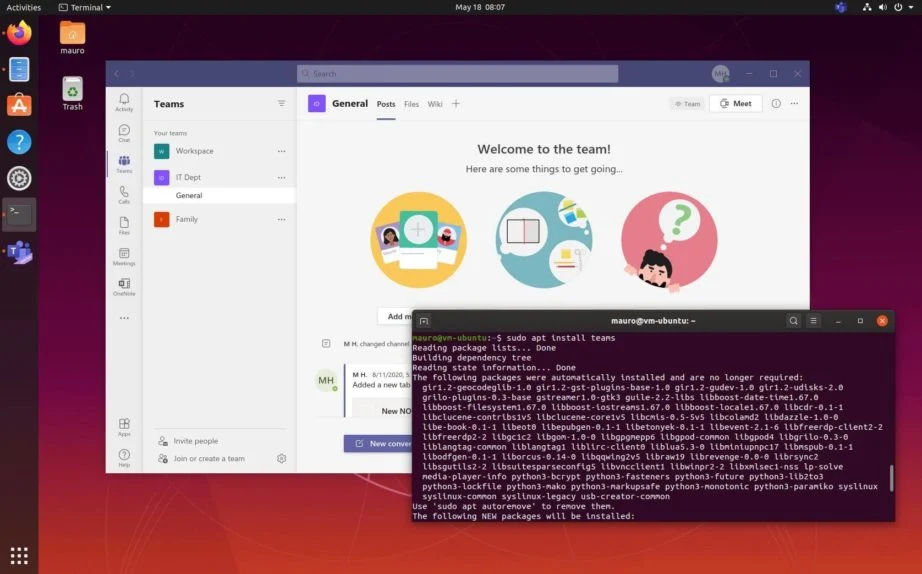
Linux users can use both the MS Teams web client and the full desktop version of Teams. The Teams desktop client for Linux has been available since December 2019. In this article, we'll see how to install the full Microsoft Teams client on various Linux distributions.
You can download the Teams distribution from the Microsoft website as ready-made .deb and .rpm packages (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-teams/download-app).
Installing the DEB or RPM package will automatically add the Microsoft Teams repositories:
- DEB https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/ms-teams stable main
- RPM https://packages.microsoft.com/yumrepos/ms-teams
It will also add the Microsoft repository PGP key (https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc) to ensure that the Microsoft Teams package (updated monthly) is automatically updated by your Linux package manager.
You can also install Teams from the terminal console. In general, on any Linux distribution, the Teams installation looks like this:
- Installing the Microsoft repository key;
- Adding a Teams repository;
- Updating the package database;
- Installing the Microsoft Teams client from the repository.
Installing Teams on Debian, Ubuntu, Mint distributions:
- Launch the terminal by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T or Ctrl + Shift + T;
- Install curl if not already done: sudo apt install curl
- Add the Microsoft repository key:
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add –
- Now we need to add the Microsoft Teams repository:
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/ms-teams stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/teams.list'
- Update the package base: sudo apt update
- Install the Teams client (you need about 300 MB of free disk space):
sudo apt install teams
- The command to update the package is:
sudo apt install teams
- To check that the ms-teams repo is in the list of repositories, run the command:
sudo grep -rhE ^deb /etc/apt/sources.list*
- Make sure the file contains the line:
deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/ms-teams stable main
- To uninstall the Teams client, use the command:
sudo apt remove teams
- Installing MS Teams in distributions based on RHEL, Fedora, CentOS uses the yum (dnf) package manager:
sudo rpm --import https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc
sudo sh -c 'echo -e "[teams]\nname=teams\nbaseurl=https://packages.microsoft.com/yumrepos/ms-teams\nenabled=1\ngpgcheck=1\ngpgkey=https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc" > /etc/yum.repos.d/teams.repo'
sudo dnf check-update
sudo dnf install teams
- Installing MS Teams on openSUSE -based distributions:
sudo rpm --import https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc
sudo sh -c 'echo -e "[teams]\nname=teams\nbaseurl=https://packages.microsoft.com/yumrepos/ms-teams\nenabled=1\nautorefresh=1\nkeeppackages=0\ntype=rpm-md\ngpgcheck=1\ngpgkey=https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc" > /etc/zypp/repos.d/teams.repo'
sudo zypper refresh
sudo zypper install teams
- Now you can launch the Teams client with the command:
teams
- Sign in to your Microsoft account.
A ready-to-use MSTeams client should open.
By default, the Teams client is set to start automatically, but you can disable it from starting automatically.
You can use the MicrosoftTeams PowerShell module to manage your Teams organization from the command line. To do this, you first need to install PowerShell Core for your Linux distribution.







Комментарии