Network adapters not showing up in Windows.

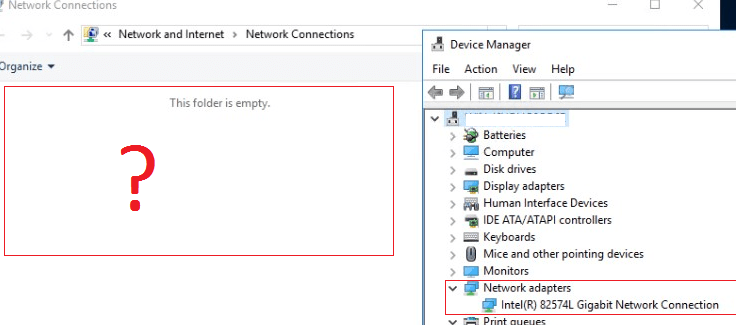
On one of the Windows hosts, after the P2V migration, I encountered the fact that all network adapters disappeared in the network connections in the Control Panel . At the same time, in the Device Manager in the Network Adapters section, you can see that the Ethernet network card is installed. In my case, the problem was solved by simply resetting the network settings using the Network Reset button in the control panel, but I decided to go further. In this article, I tried to collect typical steps that you need to check / perform if network adapters are not displayed in Windows. The instruction is as universal as possible and should help you restore network availability both in Windows 10/11 and in Windows Server.
Typical reasons why network adapters are not displayed in Windows:
- Drivers for the network card are not installed;
- Incorrect network adapter drivers installed;
- There are no physical network adapters on the computer / laptop, they are not connected or are out of order;
- Windows network stack failure.
Open Device Manager ( devmgmt.msc ) and make sure there are physical devices under Network Adapters. These can be Wi-Fi (Wireless) network adapters or wired Ethernet adapters (connections).
Ignore adapters named Wan Miniport - these are virtual network adapters used for VPN connections.
If there is no equipment in the list of network adapters, but in the Other device section there are devices Unknown device/Network Controller with yellow exclamation marks, you need to try to determine the type of these devices and install the appropriate driver. Perhaps this is your missing network adapters.
Check if automatic driver updates are disabled in Windows. Try searching for drivers automatically. Windows should itself have identified and installed the appropriate drivers.
If Windows did not agree to recognize the device, you must manually identify it. Find the VID and PID of the unknown device (Properties -> Details -> Hardware IDs). Copy the ID and search on google. For example, PCI\VEN_14E4&DEV_43A0 these are Broadcom Wireless network devices. So you can understand what kind of device it is, download and install its driver.
If the list of network adapters is empty and there are no unrecognized devices on the computer, search for devices in the manager (Action -> Scan for hardware changes).
Then check that your network card is physically connected to your computer / laptop and not disabled in the BIOS / UEFI settings. Perhaps you need to check your network device on another computer (if possible) or check its performance at a service center (perhaps it just failed).
If your network adapter shows up in Device Manager but doesn't show up in Network Connections, try uninstalling it and reinstalling it.
- Click on the network card in Device Manage and select Uninstall Device;
- Perform device discovery (Action -> Scan for hardware changes);
- Windows should find and install the most appropriate driver for the network adapter.
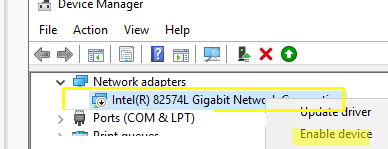
If this does not help, try manually downloading the network adapter driver from the manufacturer's website and installing it manually.Make sure the network adapter is enabled in Windows Device Manager. Disabled devices are displayed with a small down arrow icon. Enable the adapter -> Enable device.If only network adapters for wireless Wi-Fi connections are missing in Windows, you need to check that the WLAN AutoConfig service is enabled. Check the service status using PowerShell:
Get-Service WlanSvcIf the service is disabled, you need to enable it and set it to autostart:
Set-Service WlanSvc –startuptype automatic –passthru
Start-Service WlanSvc –PassThru
In Windows Server, you must manually enable the component that provides support for Wi-Fi networks in Windows Server (by default, the Wireless-Networking component is disabled).Reset network settings and network stack settings in Windows using the commands (in cmd.exe with administrator rights):
netsh winsock reset catalog
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset
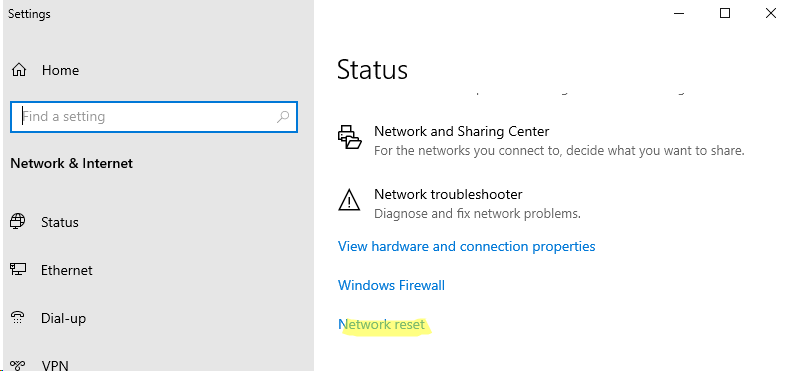
Open the network settings in the modern Settings panel (for quick access, run the command ms-settings:network ) and click the Network Reset button.
Restart your computer.
If nothing helped:- If a third-party antivirus is installed on the computer, try uninstalling it;
- Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter with the command:
msdt.exe /id NetworkDiagnosticsNetworkAdapter
- Verify the integrity of the Windows image using DISM and SFC:
sfc /scannow
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth







Комментарии